Beginner’s Guide to Using AI Tools for Email Marketing
Email marketing has remained one of the most profitable digital channels for nearly two decades. Industry research from Litmus and the Data & Marketing Association consistently reports an average return of $36–$42 for every $1 spent. Few marketing channels offer that level of measurable efficiency.
At the same time, the global email user base is projected to reach 4.6 billion users by 2025, according to Statista. The scale is enormous, and so is the competition inside the inbox.
However, while reach and ROI remain strong, user expectations have evolved. Salesforce’s State of Marketing reports show that a majority of consumers now expect personalized experiences across channels, and 77% of marketers say personalization increases engagement.
Generic batch-and-blast campaigns no longer perform the way they did a decade ago. Subscribers expect emails that reflect their behavior, preferences, timing, and purchase history. Relevance is no longer optional; it is a performance requirement.
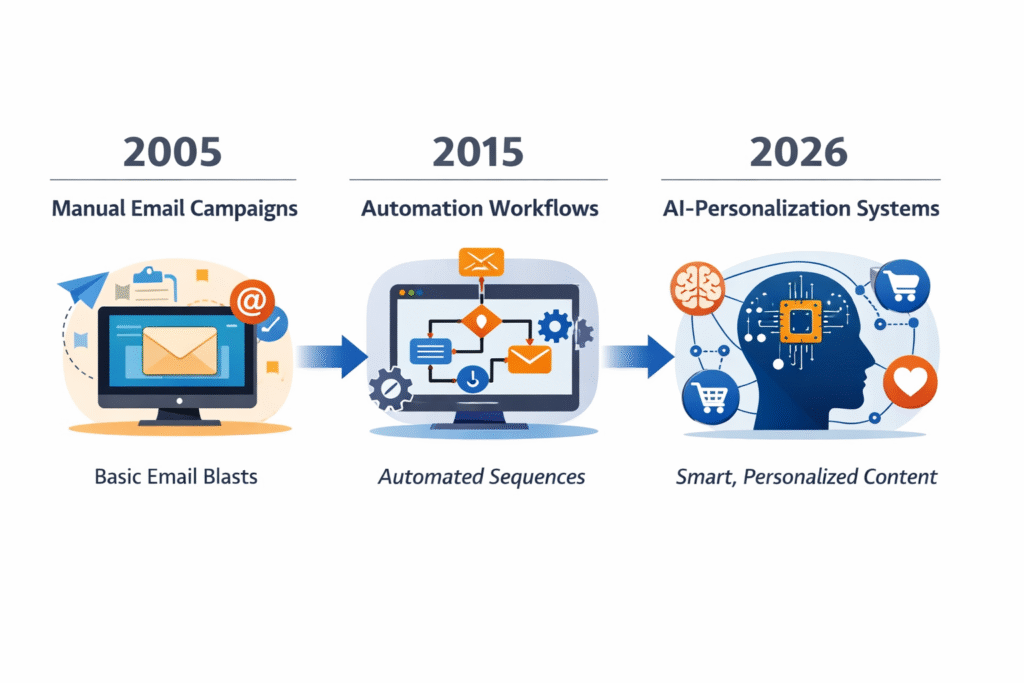
Traditional email marketing relied heavily on manual segmentation and rule-based workflows. Marketers created static lists based on basic criteria such as location, age, or past purchases. Automation rules followed fixed sequences: send Email B three days after Email A. While effective in early stages, this approach does not adapt dynamically to individual behavior.
As databases grow into tens or hundreds of thousands of contacts, manual segmentation becomes inefficient and error-prone. The larger the audience, the harder it becomes to maintain meaningful personalization using static rules.
The industry is now transitioning from rule-based automation to predictive intelligence. Instead of asking, “When should we send this email?” marketers now ask, “When is this individual most likely to open?” Instead of grouping customers manually, systems now analyze behavioral patterns in real time.
Machine learning models identify trends across engagement history, browsing activity, and transaction data. Natural language processing assists with subject line optimization and content variation. Predictive analytics estimates churn risk and lifetime value before problems become visible.
This shift represents more than a feature upgrade. It marks a structural change in how email marketing operates. AI tools for email marketing are not simply add-ons layered on top of automation software. They are becoming core infrastructure. These systems continuously learn from data inputs, adjust segmentation dynamically, optimize send times, and refine messaging based on performance feedback loops.
AI tools for email marketing are becoming a core part of modern digital marketing strategies, helping brands scale personalization and automation.
As inbox competition intensifies and privacy regulations limit broad targeting tactics, precision becomes a competitive advantage. Businesses that rely solely on manual workflows risk stagnation. Those that integrate AI-driven systems gain scalability, efficiency, and performance optimization that compound over time. Businesses that stay updated with the latest digital marketing insights are better positioned to leverage AI-powered automation.
The evolution from manual email blasts in 2005, to automation platforms in 2015, and now to AI-powered personalization in 2026 reflects a clear industry trajectory: intelligence is replacing repetition.
What Are AI Tools for Email Marketing? (Foundational Mechanics)
AI tools for email marketing are systems that use artificial intelligence to analyze behavioral data, predict user actions, personalize content, and continuously optimize campaigns without relying solely on fixed rules. To understand their real value, it is important to move beyond surface definitions and examine the mechanics that power them.
At a structural level, traditional email marketing operates on instructions written by humans. AI-driven systems, in contrast, operate on data patterns discovered by machines. The difference is not cosmetic; it fundamentally changes how decisions are made inside the email workflow.
Core Technologies Powering AI Email Systems
AI tools for email marketing are built on three primary technological pillars.
Machine Learning (Pattern Recognition and Predictive Modeling)
Machine learning algorithms analyze historical campaign data to detect patterns. For example, they can identify which subscribers open emails at specific times, which types of content drive clicks, or which behaviors indicate a high likelihood of purchase. Predictive modeling allows the system to forecast future actions, such as churn probability or conversion likelihood. Instead of reacting to past performance alone, the system anticipates outcomes.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
Natural language processing enables AI systems to understand and generate human language. In email marketing, NLP is used to optimize subject lines, evaluate tone, personalize messaging, and even generate dynamic content blocks. By analyzing engagement data, NLP models can determine which word structures, emotional triggers, or personalization elements correlate with higher open and click rates.
Behavioral Data Clustering
Behavioral clustering groups subscribers based on actions rather than static demographic attributes. Instead of segmenting by age or location alone, AI clusters users by browsing patterns, purchase frequency, engagement intensity, and lifecycle stage. These clusters update automatically as behavior changes, enabling real-time personalization.
Together, these technologies form the analytical engine behind AI tools for email marketing.
Difference Between Automation and AI
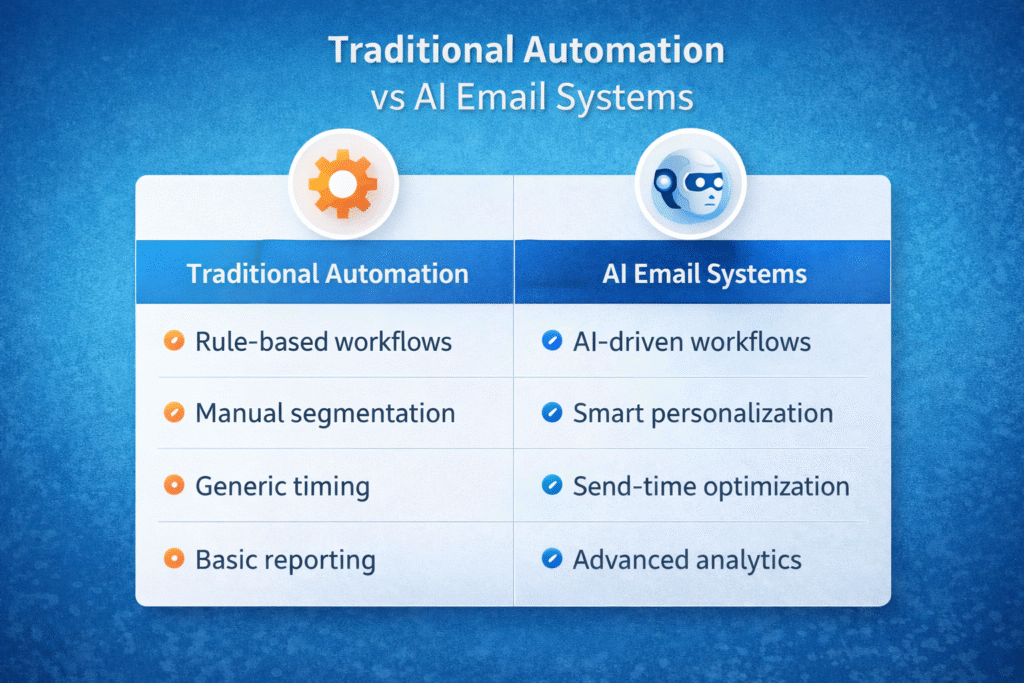
Many marketers confuse automation with artificial intelligence. While both aim to streamline campaigns, their decision-making logic differs significantly.
Rule-Based Triggers vs Adaptive Decision-Making
Traditional automation operates on predefined rules. For example: “If user downloads ebook, send follow-up email after 3 days.” The system executes instructions exactly as programmed. It does not evaluate whether 3 days is optimal for each individual.
AI systems, however, use adaptive decision-making. Instead of sending a follow-up after a fixed interval, the system predicts when the specific subscriber is most likely to engage and adjusts timing automatically. Decision logic evolves as new data is collected.
Static Segments vs Dynamic Real-Time Micro-Segmentation
Automation typically relies on static segments created manually. Once a subscriber enters a segment, they remain there until manually reassigned. This can lead to outdated targeting.
AI introduces dynamic micro-segmentation. Subscribers move between segments automatically based on current behavior. If engagement drops, the system may trigger a re-engagement sequence. If purchase intent rises, it may prioritize promotional offers. Segmentation becomes fluid rather than fixed.
The shift from rule-based execution to predictive intelligence represents the core structural evolution in email marketing systems.
Where AI Fits in the Email Workflow
AI tools for email marketing integrate into a continuous optimization loop:
Data → Prediction → Personalization → Delivery → Optimization
- Data Collection: Behavioral data, engagement metrics, purchase history, and interaction signals are captured.
- Prediction: Machine learning models analyze this data to forecast engagement likelihood, churn risk, and conversion probability.
- Personalization: Content, subject lines, and send times are dynamically tailored to individual users.
- Delivery: Emails are sent at predicted optimal times using adaptive scheduling.
- Optimization Loop: Performance metrics feed back into the system, refining future predictions.
This feedback loop transforms email marketing from a scheduled broadcast model into an adaptive intelligence system.
Traditional Automation vs AI Email Systems (Depth Comparison)
| Dimension | Traditional Automation | AI Email Systems |
| Decision Logic | Predefined rules | Predictive, data-driven decisions |
| Segmentation | Static lists | Dynamic real-time micro-segmentation |
| Send Timing | Fixed schedule | Individual predictive timing |
| Personalization | Basic merge tags | Behavioral and predictive personalization |
| Optimization | Manual A/B testing | Continuous machine learning optimization |
| Scalability | Limited by rule complexity | Scales automatically with data growth |
| Adaptability | Reactive | Proactive and anticipatory |
Understanding these foundational mechanics clarifies that AI tools for email marketing are not merely advanced automation features. They represent an architectural shift toward systems that learn, predict, and refine performance autonomously. As databases expand and personalization expectations intensify, this shift becomes less optional and more structural to competitive email strategy.
Why AI Tools for Email Marketing Deliver Higher ROI
Return on investment is the metric that ultimately determines whether a marketing channel scales or stagnates. Email marketing already delivers a strong baseline performance, but AI tools for email marketing significantly increase efficiency by optimizing the variables that most influence engagement and revenue. Rather than improving one isolated metric, AI compounds gains across open rates, click-through rates, and conversions simultaneously.
Traditional campaigns rely on periodic testing and manual adjustments. AI-driven systems operate continuously, refining outcomes in real time. This continuous optimization loop is what drives measurable ROI improvement.
Open Rate Optimization
Open rate is the first performance gate. If the email is not opened, no downstream metric matters. AI tools for email marketing improve open rates primarily through subject line optimization and predictive timing.
Machine learning models analyze historical engagement patterns to identify which phrasing structures, emotional triggers, and word lengths generate higher opens. Industry studies indicate that AI-assisted subject line optimization can improve open rates by approximately 5–10% compared to static testing models.
Beyond wording, predictive send-time optimization identifies when individual subscribers are most likely to check their inbox. Instead of sending to the entire list at 10 a.m., AI staggers delivery based on personal engagement patterns. The result is greater inbox visibility and reduced message fatigue.
Even incremental open-rate increases have a multiplicative impact on revenue when applied to large subscriber databases.
Click-Through Rate Enhancement
While open rates determine visibility, click-through rate (CTR) determines engagement depth. AI tools for email marketing enhance CTR by improving relevance at the content level.
Personalized content blocks dynamically adapt sections of the email based on subscriber behavior. For example, e-commerce users may see product categories aligned with past browsing activity. Content relevance increases interaction probability.
Dynamic calls-to-action (CTAs) adjust messaging depending on lifecycle stage. A new subscriber might see “Explore Collection,” while a returning customer sees “Complete Your Purchase.” These micro-adjustments improve alignment between intent and message.
Unlike static A/B tests that require manual analysis, AI systems continuously learn from interaction data and automatically prioritize higher-performing content variations.
Conversion and Revenue Impact
Open and click metrics ultimately matter because they influence revenue. AI tools for email marketing directly affect conversion rates through predictive modeling and timing precision.
Predictive product recommendations analyze purchase history and browsing behavior to identify items with the highest likelihood of purchase. Rather than promoting generic offers, the system highlights individualized recommendations.
Send-time optimization ensures offers are delivered when purchase intent is highest. For example, a subscriber who frequently engages in the evening may receive promotional emails during that window, increasing the probability of immediate action.
Additionally, AI can identify high-value subscribers and prioritize retention campaigns, reducing churn and increasing lifetime value. Revenue growth, therefore, is not limited to short-term conversion spikes but extends to long-term customer relationships.
Case Scenario Walkthrough: Before AI vs After AI
Consider a simplified model:
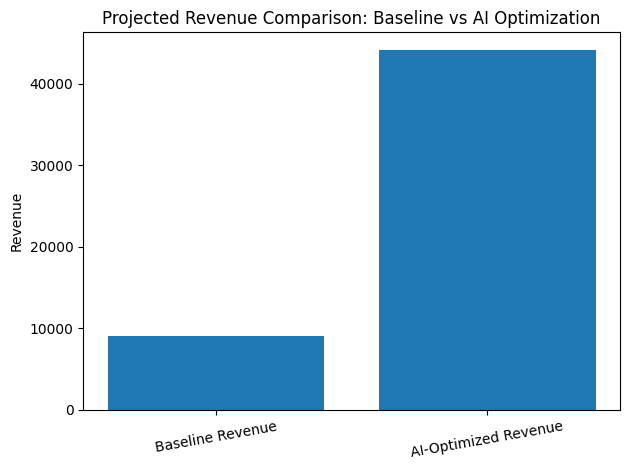
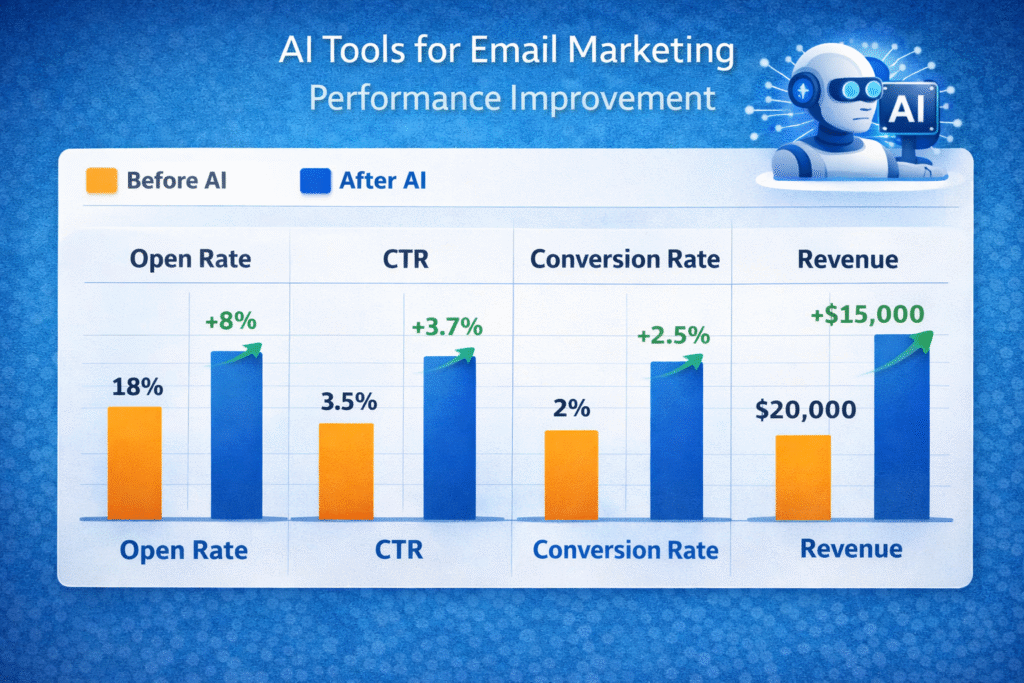
Before AI Implementation
- Subscriber base: 50,000
- Open rate: 18%
- Click-through rate: 2.5%
- Conversion rate: 1.2%
- Revenue per campaign: $12,000
After AI Implementation
- Open rate increases by 8% (to 19.4%)
- CTR increases by 20% (to 3%)
- Conversion rate improves to 1.5% through predictive targeting
- Revenue per campaign rises proportionally to approximately $16,000–$18,000
Even modest improvements at each stage create a compounding revenue effect. When applied across multiple campaigns annually, the total ROI lift becomes substantial.
The power of AI tools for email marketing lies in this compounding mechanism. Each stage of the funnel improves incrementally, and the cumulative impact drives higher profitability without proportionally increasing marketing spend.
Core Features of AI Tools for Email Marketing (Deep Functional Breakdown)
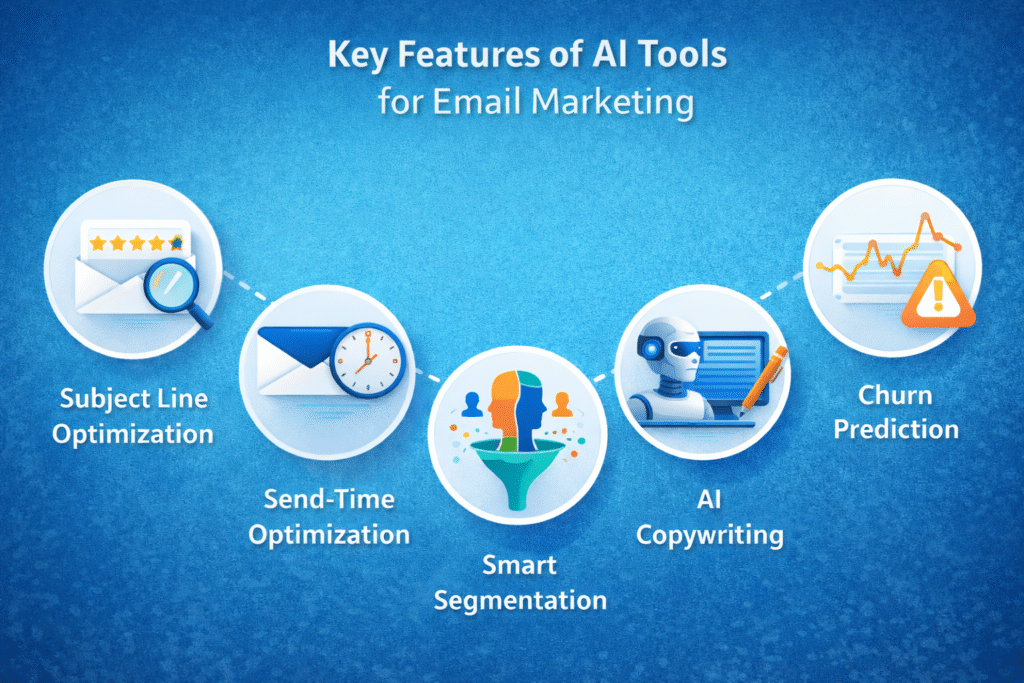
To understand the real value of AI tools for email marketing, it is necessary to examine how their core features operate beneath the interface. These systems are not simple automation upgrades; they rely on predictive modeling, behavioral analysis, and continuous optimization loops. Each feature contributes differently to performance, scalability, and ROI.
AI Subject Line Optimization
What it does:
Improves open rates by generating and refining subject lines that are statistically more likely to attract attention.
How it works:
Machine learning models analyze historical campaign data, including open rates, click patterns, word usage, emotional tone, and character length. Natural language processing evaluates phrasing structures and predicts engagement probability. Some platforms continuously test variations and automatically prioritize high-performing formats.
When to use it:
Ideal for high-volume campaigns where incremental open-rate gains significantly impact revenue. Particularly effective in promotional, e-commerce, and newsletter campaigns.
Risk or limitation:
Over-optimization may lead to sensationalized or repetitive phrasing. Performance also depends on sufficient historical data to train the model effectively.
Predictive Send-Time Optimization
What it does:
Determines the optimal delivery time for each subscriber to maximize open probability.
How it works:
AI systems analyze past engagement timestamps to identify when individuals are most active in their inbox. Instead of batch delivery, emails are scheduled dynamically based on predicted engagement windows.
When to use it:
Best for large subscriber lists across different time zones or varied behavioral patterns. Particularly valuable for global businesses.
Risk or limitation:
Limited effectiveness for new subscribers without historical interaction data. Requires consistent tracking of engagement metrics.
Smart Behavioral Segmentation
What it does:
Creates dynamic audience groups based on real-time behavior rather than static demographics.
How it works:
Behavioral signals such as browsing activity, purchase frequency, email clicks, and website interactions are clustered using machine learning algorithms. Subscribers automatically move between segments as their behavior changes.
When to use it:
Highly effective for e-commerce, SaaS, and subscription-based businesses where user intent evolves rapidly.
Risk or limitation:
Data quality is critical. Incomplete CRM integration or inconsistent tracking reduces segmentation accuracy.
AI Copywriting Assistance
What it does:
Generates personalized subject lines, body content, and dynamic content blocks aligned with engagement patterns.
How it works:
Natural language processing models analyze tone, structure, and engagement trends to suggest optimized messaging. Some tools personalize content blocks based on behavioral data or lifecycle stage.
When to use it:
Useful for teams managing frequent campaigns or scaling personalized messaging without increasing manual workload.
Risk or limitation:
Requires human oversight to maintain brand consistency and avoid generic output. AI-generated content should always be reviewed before deployment.
Churn Prediction Models
What it does:
Identifies subscribers who are likely to disengage or unsubscribe.
How it works:
Machine learning evaluates declining open rates, inactivity periods, reduced website visits, and purchase gaps. Subscribers are assigned churn probability scores, triggering automated retention campaigns when risk thresholds are crossed.
When to use it:
Essential for subscription services, SaaS platforms, and businesses focused on lifetime value optimization.
Risk or limitation:
Accuracy depends on the depth of historical behavioral data. Short customer lifecycles may reduce predictive precision.
Lifecycle Journey Automation
What it does:
Automates email sequences aligned with each stage of the customer lifecycle, from acquisition to retention.
How it works:
AI evaluates behavioral milestones and engagement signals to adjust journey paths dynamically. Messaging adapts based on purchase activity, engagement frequency, and predicted intent.
When to use it:
Effective for businesses with complex funnels, onboarding processes, or multi-step conversion paths.
Risk or limitation:
Implementation can be technically complex, requiring robust CRM integration and clearly defined lifecycle stages.
Feature Comparison Table
| Feature | Required Data | Performance Impact | Complexity Level |
| AI Subject Line Optimization | Historical open-rate and engagement data | 5–10% open-rate improvement potential | Low–Medium |
| Predictive Send-Time Optimization | Engagement timestamps and behavioral logs | Higher open rates and improved timing precision | Medium |
| Smart Behavioral Segmentation | CRM data, browsing behavior, purchase history | Increased CTR and improved targeting accuracy | Medium–High |
| AI Copywriting Assistance | Brand guidelines, engagement benchmarks | Faster production and personalized messaging | Low–Medium |
| Churn Prediction Models | Long-term engagement and inactivity patterns | Reduced churn and higher retention rates | High |
| Lifecycle Journey Automation | Multi-touch behavioral data and CRM integration | Higher lifetime value and funnel efficiency | High |
Collectively, these features demonstrate that AI tools for email marketing function as adaptive systems rather than static automation platforms. Each capability enhances a specific performance variable—open rates, engagement, retention, or revenue—while feeding into a continuous optimization loop. When supported by accurate data and strategic oversight, these tools transform email marketing from a scheduled broadcast channel into an intelligent growth engine.
Step-by-Step Beginner Implementation Framework
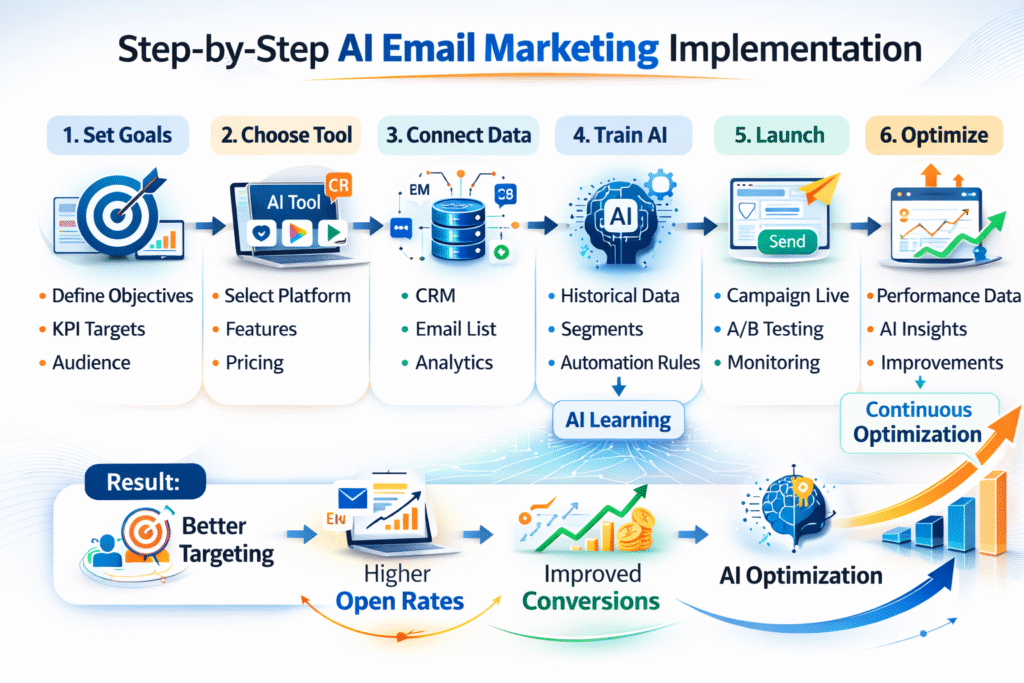
Adopting AI tools for email marketing can feel technically intimidating for beginners. The key to frictionless execution is structure. Instead of activating every AI feature at once, implementation should follow a phased framework that prioritizes clarity, clean data, and measurable results. Below is a practical roadmap designed to reduce overwhelm and increase performance stability.
Step 1 — Define Campaign Objectives & KPIs
Before selecting tools or activating AI features, define the purpose of the campaign. AI performs best when objectives are specific and measurable.
Common campaign goals include:
- Increase open rate by 8–10%
- Improve click-through rate by 15%
- Boost conversion rate for a product launch
- Reduce churn by 5% over 90 days
Mini-checklist:
- Define primary goal (engagement, revenue, retention)
- Select 2–3 KPIs (open rate, CTR, conversion rate, revenue per email)
- Establish baseline metrics for comparison
- Set realistic improvement targets
Common failure point: launching AI campaigns without clear success metrics. Without benchmarks, performance gains cannot be measured accurately.
Step 2 — Choose AI Email Platform (Criteria Framework)
Selecting the right platform should be based on operational fit, not feature volume.
Evaluation criteria:
- Integration capability with CRM and website
- Availability of predictive analytics
- Ease of use for beginners
- Scalability for list growth
- Transparent pricing structure
Mini-checklist:
- Confirm CRM compatibility
- Review data import/export capabilities
- Test AI feature demos before commitment
- Ensure reporting dashboard clarity
Common failure point: choosing overly complex platforms that exceed team capability, leading to underutilized features.
Step 3 — Data Preparation & Hygiene
AI systems rely entirely on data accuracy. Poor data hygiene undermines predictive precision.
Tasks to complete:
- Remove inactive or invalid email addresses
- Standardize data fields (e.g., naming conventions)
- Merge duplicate contacts
- Tag behavioral data consistently
- Confirm consent and compliance status
Mini-checklist:
- Audit subscriber database
- Clean bounce-heavy segments
- Verify tracking pixels and analytics integration
- Ensure GDPR and compliance standards are met
Common failure point: skipping data cleaning before training the AI model, resulting in flawed segmentation and inaccurate predictions.
Step 4 — Training the AI Model
Once data is prepared, the system must analyze historical performance patterns.
Training inputs typically include:
- Past open and click rates
- Purchase history
- Website browsing behavior
- Engagement timestamps
The AI model identifies behavioral trends and engagement probabilities. The longer the data history, the more accurate predictive outputs become.
Mini-checklist:
- Upload at least 3–6 months of historical campaign data
- Activate predictive segmentation features
- Monitor initial AI-generated insights before campaign launch
Common failure point: expecting immediate optimization results without allowing sufficient learning time.
Step 5 — Launch Pilot Campaign
Avoid full-scale rollout initially. Begin with a controlled pilot campaign to validate system performance.
Example campaign workflow:
- Select a segment (e.g., repeat customers)
- Activate AI subject line optimization
- Enable predictive send-time feature
- Use dynamic content personalization
- Compare results against the previous manual campaign
Mini-checklist:
- Limit the pilot audience to a manageable size
- Track baseline vs AI-driven metrics
- Monitor deliverability and engagement daily
- Avoid changing multiple variables simultaneously
Common failure point: launching multiple AI features at once without isolating impact, making it difficult to identify performance drivers.
Step 6 — Performance Analysis & Iteration
After the pilot campaign, analyze performance data systematically.
Metrics to evaluate:
- Open rate improvement percentage
- CTR change relative to baseline
- Conversion rate difference
- Revenue lift per subscriber
- Unsubscribe rate trends
AI tools for email marketing improve over time through feedback loops. Performance analysis should inform iterative adjustments.
Mini-checklist:
- Compare pilot results against baseline benchmarks
- Identify high-performing segments
- Expand successful configurations gradually
- Schedule monthly optimization reviews
Common failure point: treating AI as a one-time activation rather than an ongoing optimization process.
Example AI Campaign Execution Flow (Diagram Concept)
Data Collection
→ Data Cleaning & Structuring
→ AI Model Training
→ Predictive Segmentation
→ Personalized Content Generation
→ Predictive Send-Time Delivery
→ Performance Tracking
→ Continuous Optimization Loop
This execution flow demonstrates how AI tools for email marketing transform traditional linear campaigns into adaptive systems. Each stage feeds the next, creating a self-improving cycle.
By following this structured framework—objective definition, platform selection, data preparation, model training, pilot testing, and iterative refinement—beginners can implement AI without operational disruption. The focus remains on clarity, measurable impact, and gradual scalability rather than complexity for its own sake.
Comparing the Best AI Tools for Email Marketing

Choosing the right AI tool for your email marketing strategy is more than reading hype from product pages. Each platform approaches artificial intelligence differently, with strengths shaped by data architecture, integration depth, and practical use cases. Below is a realistic comparison of four leading options — not marketing claims, but how they actually perform in the real world.
Mailchimp AI
Mailchimp is often the first stop for beginners because it combines familiar email marketing basics with AI-powered enhancements. It doesn’t reinvent the wheel, but it brings practical intelligence that small teams can use without heavy technical setup.
AI Strength:
Good at subject line suggestions and send-time prediction based on basic engagement patterns.
Real positioning note: While its AI is useful, it’s not as deep as enterprise systems — it leverages straightforward ML signals rather than advanced predictive engines.
Ideal for:
Small businesses, solopreneurs, and beginners who need an easy learning curve.
Limitations:
Requires significant historical data for accurate predictions, and advanced features are limited compared to mid-market tools.
HubSpot Email AI
HubSpot’s AI capabilities sit inside a full CRM ecosystem. This integration is its biggest advantage because AI has access to richer customer signals like lifecycle stage, page behavior, and sales interactions.
AI Strength:
Holistic personalization and adaptive workflows powered by combined CRM + email data. Behaviors and predictions are layered across email, sales, and web interactions.
Ideal for:
Growing small-to-medium businesses and teams that want marketing and sales alignment.
Limitations:
Steeper learning curve and higher cost. New users can feel overwhelmed by feature depth.
Klaviyo Predictive Engine
Klaviyo has become a strong choice for e-commerce brands because it excels at turning transactional and behavioral data into actionable predictions.
AI Strength:
Predictive segmentation, product recommendations, and lifecycle targeting based on purchase history, browsing data, and multi-touch behavior.
Ideal for:
E-commerce businesses with strong data flows (web tracking + purchase histories).
Limitations:
Less beginner-friendly; requires solid data collection infrastructure to unlock full value.
ActiveCampaign AI
ActiveCampaign blends advanced automation with AI signals without sacrificing usability. Its strength lies in predictive actions layered into automated journeys.
AI Strength:
Predictive sending, smart segmentation, and predictive customer scoring within complex automation paths.
Ideal for:
Small and mid-sized businesses that need scalable automation without jumping fully into enterprise territory.
Limitations:
AI features are powerful but require thoughtful setup and planning, or users may underutilize them.
Comparison Table
| Tool | AI Strength | Ideal Business Size | Learning Curve | Data Requirements |
| Mailchimp AI | Subject line optimization, send-time predictions | Small businesses, solopreneurs | Easy | Low-medium (needs engagement history) |
| HubSpot Email AI | CRM-driven personalization and adaptive workflows | SMBs with sales + marketing alignment | Moderate-high | High (needs CRM + behavioral data) |
| Klaviyo Predictive Engine | Predictive segmentation + product recommendations | E-commerce businesses | Moderate | High (transactional + behavioral data) |
| ActiveCampaign AI | Predictive automation + scoring | SMBs scaling automation | Moderate | Medium-high |
Realistic Positioning Notes (Not Marketing Claims)
- Mailchimp’s AI is practical but entry-level. Its predictions are good for improving engagement without heavy setup, but it doesn’t rival tools that draw from CRM and behavior deeply.
- HubSpot’s AI becomes more powerful when you leverage its CRM data deeply. Its personalization can be more strategic than tactical.
- Klaviyo’s strength is prediction rooted in purchase behavior. It excels in e-commerce environments, but lacks a broader CRM context unless integrated.
- ActiveCampaign sits in the middle — stronger AI than basic tools, but more accessible than high-end enterprise platforms.
In short: if you’re just starting, Mailchimp is easiest; if you’re scaling with sales, HubSpot adds strategic depth; if you run e-commerce, Klaviyo drives revenue-centric personalization; and ActiveCampaign is the balanced choice for automation depth with manageable complexity.
Real-World Use Cases (Deep Application Layer)
Understanding AI tools for email marketing becomes clearer when applied to real operational scenarios. Below are high-impact use cases where artificial intelligence moves beyond theory and directly influences measurable outcomes.
E-commerce Personalization Engines
Problem:
E-commerce brands often struggle with abandoned carts, low repeat purchases, and generic promotional blasts that fail to convert diverse customer segments. Traditional segmentation by category or purchase history rarely captures real-time intent.
AI Intervention:
AI tools analyze browsing behavior, purchase frequency, cart additions, and engagement timestamps. Predictive recommendation engines identify products with the highest probability of purchase. Dynamic content blocks personalize offers, discounts, and cross-sell items. Predictive send-time optimization ensures promotional emails arrive during peak engagement windows.
Measurable Improvement:
Brands commonly see higher click-through rates due to product relevance, reduced cart abandonment, and increased average order value. Even modest improvements in personalization can lift conversion rates significantly when scaled across large subscriber bases.
Risk:
Over-personalization may feel intrusive if data usage lacks transparency. Poor tracking accuracy can lead to irrelevant recommendations, reducing trust.
SaaS Onboarding Sequences
Problem:
SaaS companies frequently experience drop-offs during onboarding. New users sign up but fail to complete activation steps, reducing long-term retention and lifetime value.
AI Intervention:
AI monitors in-app behavior, login frequency, and feature usage. Based on engagement patterns, it adjusts onboarding email sequences dynamically. For example, inactive users may receive tutorial-focused emails, while active users receive feature-advancement content. Churn prediction models identify users at risk of early disengagement.
Measurable Improvement:
Improved feature adoption rates, higher activation percentages, and reduced early churn. By aligning messaging with real-time user behavior, onboarding becomes adaptive rather than static.
Risk:
Requires strong product analytics integration. Without accurate behavioral tracking, onboarding personalization loses precision.
Lead Nurturing Funnels
Problem:
B2B and service-based businesses often generate leads that go cold due to poorly timed follow-ups or generic email sequences. Manual segmentation fails to prioritize high-intent prospects.
AI Intervention:
AI scores leads based on engagement frequency, content downloads, website visits, and interaction depth. Predictive models estimate purchase likelihood. High-intent leads receive more targeted and timely follow-ups, while lower-intent leads remain in educational sequences. AI-powered subject lines and dynamic CTAs adjust messaging according to funnel stage.
Measurable Improvement:
Higher conversion rates from marketing-qualified leads to sales-qualified leads. Shorter sales cycles due to improved timing and personalization.
Risk:
Inaccurate scoring models can misclassify leads, causing premature sales outreach or missed opportunities.
Re-Engagement Campaigns
Problem:
Subscriber lists naturally decay over time. Inactive users lower engagement rates and harm deliverability performance. Manual re-engagement attempts often lack precision.
AI Intervention:
Churn prediction models identify declining engagement signals such as reduced opens, click inactivity, or website disengagement. AI triggers targeted re-engagement emails with tailored incentives, content reminders, or surveys. Send-time optimization increases the likelihood of visibility during reactivation attempts.
Measurable Improvement:
Higher reactivation rates, reduced unsubscribe percentages, and improved list hygiene. Successful re-engagement increases long-term revenue per subscriber.
Risk:
Excessive targeting of disengaged users may lead to higher unsubscribe rates if messaging is poorly aligned with user expectations.
Across these use cases, AI tools for email marketing function as adaptive intelligence systems rather than static automation platforms. They identify patterns in behavioral data, adjust communication strategies in real time, and refine outcomes through feedback loops. When implemented strategically and supported by clean data infrastructure, AI-driven email campaigns move beyond incremental improvements and create sustained performance gains across engagement, conversion, and retention metrics.
Measuring Success — KPIs for AI-Driven Email Marketing
Implementing AI tools for email marketing only creates value if performance improvements are measurable. Artificial intelligence enhances engagement and revenue, but those gains must be evaluated against baseline benchmarks. The goal is not simply higher metrics, but sustainable and attributable growth.
AI-driven email systems influence multiple layers of the funnel simultaneously. Therefore, success measurement should extend beyond open rates and include engagement quality, revenue impact, and attribution clarity.
Open Rate Benchmarks
Open rate remains the first performance indicator. Industry averages vary by sector, but most email campaigns fall within the 18–25% range. AI-powered subject line optimization and predictive send-time features typically produce incremental lifts of 5–10%.
For example:
- Baseline open rate: 20%
- AI-optimized open rate: 22–24%
Although the percentage increase may appear modest, improvements at scale significantly expand downstream conversion opportunities. Open rate optimization is particularly impactful for large subscriber lists where small percentage gains translate into thousands of additional views.
CTR Benchmarks
Click-through rate (CTR) reflects content relevance and call-to-action effectiveness. Average CTR across industries generally ranges between 2–4%.
AI tools improve CTR through:
- Behavioral segmentation
- Dynamic content personalization
- Predictive recommendations
- Lifecycle-specific CTAs
AI-optimized campaigns often achieve 15–25% relative CTR improvements. For example:
- Baseline CTR: 3%
- AI-enhanced CTR: 3.5–4%
CTR is often a stronger indicator of meaningful engagement than open rate because it signals active interest rather than passive visibility.
Revenue Per Subscriber
Revenue per subscriber (RPS) is one of the most critical performance indicators for AI-driven campaigns. It measures total revenue generated divided by the number of active subscribers.
AI contributes to RPS growth through:
- Predictive product recommendations
- Purchase-intent scoring
- Targeted upsell and cross-sell messaging
- Reduced churn via retention modeling
Even small increases in average order value or repeat purchase frequency can raise RPS significantly over time. For example:
- Baseline RPS: $2.40 per campaign
- AI-optimized RPS: $2.80–$3.20 per campaign
Compounded over multiple campaigns annually, the revenue lift becomes substantial.
AI Attribution Modeling
Traditional email reporting often attributes conversions only to last-click interactions. AI attribution modeling provides a more nuanced understanding by evaluating multiple touchpoints across the customer journey.
AI-driven attribution can:
- Assign weighted credit across email sequences
- Identify which content variations contribute most to conversions
- Predict long-term lifetime value influenced by email engagement
This allows marketers to move beyond surface metrics and evaluate how AI-driven personalization impacts full-funnel revenue contribution. Attribution clarity also improves budget allocation decisions.
Industry Benchmarks vs AI-Optimized Benchmarks
| KPI | Industry Benchmark | AI-Optimized Benchmark | Typical Improvement Range |
| Open Rate | 18–25% | 22–28% | 5–10% relative lift |
| Click-Through Rate | 2–4% | 3–5% | 15–25% relative lift |
| Conversion Rate | 1–3% | 1.5–4% | 10–30% improvement |
| Revenue Per Subscriber | Varies by industry | +10–25% increase | Compounded revenue growth |
| Churn Rate | Baseline dependent | Reduced by 5–15% | Improved retention |
Measuring success in AI-driven email marketing requires a layered evaluation model. Open rates signal visibility, CTR reflects engagement, revenue per subscriber measures profitability, and attribution modeling clarifies contribution across the funnel. AI tools for email marketing do not simply improve one metric—they create incremental gains across multiple performance variables, resulting in compounded ROI over time.
Limitations, Risks, and Ethical Considerations
While AI tools for email marketing deliver measurable performance gains, they are not without limitations. Artificial intelligence should be positioned as an amplifier of strategic marketing decisions—not a replacement for human judgment. Overreliance without oversight can introduce compliance risks, reputational damage, and operational inefficiencies.
Data Privacy & Compliance (GDPR Implications)
AI systems depend on large volumes of behavioral and transactional data. This raises compliance considerations, especially under regulations such as GDPR and other data protection frameworks. Marketers must ensure explicit consent, transparent data usage policies, and secure data storage practices. Behavioral tracking without proper disclosure can expose businesses to legal risk. AI-driven personalization must operate within clearly defined compliance boundaries, particularly when processing sensitive user data.
Over-Automation Risk
Automation improves efficiency, but excessive automation can reduce brand authenticity. AI-generated subject lines, dynamic content, and automated workflows may become repetitive or impersonal if not monitored. Customers can detect formulaic messaging patterns over time. Human review is necessary to maintain tone consistency, creativity, and contextual awareness. AI enhances scale, but strategy and brand voice require human oversight.
Model Bias & Segmentation Errors
AI models are only as accurate as the data used to train them. Incomplete, outdated, or skewed datasets can lead to segmentation errors or biased predictions. For example, churn models may incorrectly classify valuable customers as disengaged if historical signals are misinterpreted. Continuous monitoring and periodic validation of predictive outputs are essential to avoid strategic missteps.
Deliverability & Spam Concerns
Aggressive optimization tactics can inadvertently affect deliverability. Over-testing subject lines or triggering high-frequency campaigns based solely on predictive models may increase spam complaints or unsubscribe rates. Inbox placement depends on sender reputation, engagement consistency, and content quality. AI tools for email marketing must operate within sustainable sending practices to preserve long-term deliverability health.
Ultimately, AI functions as a performance amplifier. It processes data faster and identifies patterns more accurately than manual workflows, but it does not replace strategic thinking, compliance responsibility, or ethical decision-making. Businesses that combine AI efficiency with human oversight are better positioned to balance personalization, compliance, and sustainable growth.
Future Trends in AI Email Marketing (2026–2030 Outlook)
AI is rapidly shifting from a support feature to the core engine behind email marketing strategy. Between 2026 and 2030, businesses will move beyond simple automation and into predictive, self-optimizing systems powered by AI tools for email marketing. The focus will shift from sending campaigns to engineering personalized revenue journeys at scale. The rise of AI in digital marketing is transforming how brands approach personalization and automation across channels.
Hyper-Personalized Micro-Segmentation
Traditional segmentation divides audiences into broad categories like age, gender, or location. AI enables micro-segmentation, where audiences are grouped based on behavioral patterns, browsing history, purchase intent, and engagement probability. Instead of sending one message to 10,000 subscribers, marketers can deliver slightly different versions to hundreds of micro-clusters. This increases relevance, which directly impacts open rates, click-through rates, and long-term retention.
Predictive Lifetime Value Modeling
AI tools for email marketing are increasingly using predictive models to estimate a customer’s lifetime value (LTV). This allows brands to prioritize high-value subscribers, tailor premium offers, and optimize retention strategies. Rather than treating every subscriber equally, AI helps allocate budget and personalization efforts where long-term revenue impact is highest.
AI-Generated Dynamic Content Blocks
Dynamic content is becoming more intelligent. AI can now assemble email components—product recommendations, headlines, offers, and CTAs—in real time based on user behavior. Instead of manually creating multiple versions, marketers build modular templates that AI customizes for each recipient. This dramatically improves scalability without sacrificing personalization.
Multimodal and Interactive Email
Interactive emails powered by AMP and advanced design frameworks allow users to browse products, complete forms, or interact with content directly inside the email. As adoption grows, email will feel less like a static message and more like a mini web experience.
By 2030, AI tools for email marketing will not just optimize campaigns—they will continuously learn, predict, and refine performance automatically. The brands that invest early in data quality, predictive modeling, and experimentation will scale faster and build stronger customer relationships in the process.
What are AI tools for email marketing?
AI tools for email marketing use machine learning and automation to optimize subject lines, segment audiences, personalize content, and improve campaign performance. They help marketers send smarter emails based on user behavior rather than manual rules.
How do AI tools improve email open rates?
AI analyzes historical engagement data to predict which subject lines, send times, and audience segments are most likely to open emails. This data-driven optimization typically increases open rates and reduces guesswork.
Are AI email marketing tools suitable for beginners?
Yes. Most modern platforms offer beginner-friendly dashboards and automation templates. Beginners can start with basic features like send-time optimization and gradually adopt advanced AI capabilities.
Do AI tools replace human email marketers?
No. AI enhances efficiency but still requires human strategy, creativity, and brand voice oversight. The best results come from combining AI automation with human decision-making.
How much data is needed for AI email marketing to work effectively?
AI performs best with historical engagement data, but many tools can start generating insights with even a few thousand subscribers. Accuracy improves as more campaign data accumulates.
What is predictive email marketing?
Predictive email marketing uses AI to forecast subscriber behavior—such as likelihood to open, click, or churn—so marketers can send more relevant and timely emails.
Are AI email marketing tools expensive?
Pricing varies widely. Many platforms offer free or low-cost starter plans, while advanced AI features are typically included in mid-tier or premium subscriptions.
Can AI help with email personalization?
Yes. AI can dynamically personalize subject lines, product recommendations, send times, and content blocks based on individual user behavior and preferences.
Will AI improve email conversion rates?
When implemented correctly, AI-driven segmentation and personalization often improve click-through rates and conversions by delivering more relevant messages to each subscriber.
What is the biggest mistake when using AI in email marketing?
The most common mistake is over-automation without monitoring results. Marketers should regularly review AI-driven campaigns, maintain clean data, and ensure messaging stays aligned with brand voice.
The most common mistake is over-automation without monitoring results. Marketers should regularly review AI-driven campaigns, maintain clean data, and ensure messaging stays aligned with brand voice.
The most common mistake is over-automation without monitoring results. Marketers should regularly review AI-driven campaigns, maintain clean data, and ensure messaging stays aligned with brand voice.
💡 Interested in learning more? Contact RKDMT – Raju Kumar Digital Marketer (Best Digital Marketing Training Institute)
🔗 www.rajukumardigitalmarketer.com
📞 +91-7303933302 | +91-9217057127
📧 rkdmt@rajukumardigitalmarketer.com

Founder at Digital Marketing Marvel | Founder at RKDMT – Raju Kumar Digital Marketing Trainer | Best Digital Marketing Trainer in Delhi/NCR – Digiperform | Project Manager | 5+ years | Genius Study Abroad & Inlingua’s Digital Marketing Head | Learn Digital Marketing